Top AI recruiting tools and software of 2024 - TechTarget
AI is everywhere. According to a 2023 survey by HR software vendor Engagedly, AI adoption is growing rapidly, automating repetitive tasks and improving decision-making processes as well as the overall employee experience. In the survey, 81% of HR leaders have explored or implemented AI to improve process efficiency in their organizations while around 45% of HR professionals are using AI for HR management and 39% plan to use it in the near future. Nearly two-thirds of respondents said AI has greatly improved efficiency and productivity in HR.
Buyers have every right to be confused. In recruiting alone, there are well over 100 AI-based talent acquisition products in the market. AI now underlies at least part of the familiar names in talent acquisition -- for example, ICIMS, Oracle Recruiting Cloud and Workday -- as well as smaller relative newcomers, such as Onwelo's Hello Astra, Wade & Wendy, CVViZ, Findem, AmazingHiring and Manatal.
To a certain extent, AI-based recruiting products are more similar than different. A buyer is likely able to successfully source, engage, screen, hire and onboard job candidates with almost any of the popular systems, and most provide personalization capabilities, chatbots and sophisticated content creation tools. AI provides the ability to search more widely across many more sources of candidates than humans have time for, creating talent pools that are more diverse. AI can match and rank candidates to requisitions in an instant as well as search the employee population for internal candidates.
In addition, candidate engagement is improved by intelligent chatbots, which are often able to understand spoken input as well as text -- and by the newfound ease of customization from using AI for correspondence.
This article is part of
Of the 172 HR practitioners who responded to IDC's November 2022 AIPath survey, 32% named candidate matching and selection as the top AI use case for their organization. Respondents reported that when used for recruiting, AI immediately made HR's job easier, provided good insights and improved the employee experience. It also streamlined tasks and made the manager's job easier, resulting in greater efficiency, fewer steps and reduced operating costs.
Also of interest, however, is how quickly AI has spread from recruiting platforms to broader-use talent management platforms. Now, AI goes beyond focusing on ascertaining skills in initial hiring to identify skill gaps and recommend solutions, thus facilitating employees' career development. Today's most competitive AI-based applicant tracking systems (ATSes) have crossed that barrier into post-hiring skill identification and development, a promising aid to internal mobility, succession planning, and ultimately, employee retention.
Engaging engagement
Generative AI is a breakout product that has made significant headway this year, especially in areas of great use to recruiters, such as candidate engagement. With the ChatGPT bot as its poster child, generative AI excels at content creation, whether it be text, images, artwork or even videos. This is proving a godsend to both recruiters and hiring managers, who can use the technology to make job reqs more appealing, more easily customize candidate communication, and personalize job-offer and rejection letters.
Generative AI is both a time saver for recruiters and a source of inspiration for anyone seeking a kickstart to creating compelling prose, be it for formal communication, email, chatbot or text correspondence. Uses are not limited to candidate communication, however. Today's AI-based applications can generate customized pre-screening questions as well as interview guides focused on the position and candidate in question.
The key here, as always, is that human input, monitoring and sometimes intervention are required. Other AI applications are more specific and intended to augment the functionality in a traditional ATS. Examples include Eightfold AI for skills and insights; Fuel50 for workforce mobility and talent management; VONQ for branded recruitment marketing; HiredScore, which has a strong focus on compliance and ethics; and Textio, which provides language guidance for inclusive and diverse hiring.
Some products are more tailored to specific industries. HireEZ (formerly Hiretual), for example, targets healthcare and technology professionals, and stores data on relationships of people and places. Staffing Engine is designed for use by staffing firms, while Codility and HackerRank (hardly a newcomer) are used to objectively assess software developer skills.
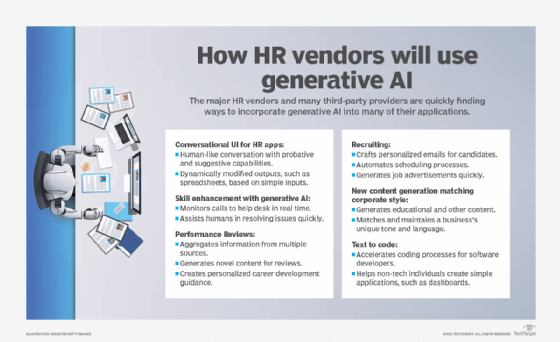
Using chatbots for recruiting is now mainstream
Conversational chatbots were early common applications of AI in talent acquisition products. Widely available for mobile devices, career sites and sometimes smartwatches, bots are increasingly relied upon to get potential candidates the focused information they need and walk them through job discovery, the application and often the onboarding process.
Chatbots, such as Paradox's Olivia, Eightfold AI's Amy and StepStone's Mya are increasingly sophisticated and friendly. Most bots can help navigate career sites, bringing pertinent jobs to the site visitor, and assist in the application process. They then manage interview scheduling, calendar coordination and sending reminders to relevant parties.
AI-based sourcing products -- Arya by Leoforce is one example -- provide a consolidated candidate communication dashboard, an essential tool for engaging and keeping track of voice, text, email and chatbot conversations. This capability is important because too often, candidate communication is lost in Post-it notes.
Using AI to funnel the most likely candidates to recruiters has become universal, without the biases surrounding age, gender, religion, race or ethnicity. This basic source, post, search, parse and match capability underlies all the talent acquisition products reviewed here and the majority in the market.
How is AI used in recruiting?
AI technology can look like old-fashioned search on steroids, and indeed, AI-enabled sourcing software can locate, deliver and filter huge volumes of data -- but more rapidly and accurately than ever before possible. Referred to as traditional AI by some, this data-provision capability is different from the generative AI that has been top of mind in the past year. Generative AI (ChatGPT is just one example) is the kind that is so useful in creating job descriptions and personalized correspondence.
It is important to understand how the engines work. To provide Day One value, the vendor has to have done extensive back-end work to avoid a cold start for the customer.
From the millions of records from which the engine learns, the vendor will create a model that will need to be validated repeatedly to ensure accurate results. This pretrained model and companion language-processing software "know" how to use a customer's own data to build a model tailored to that customer. More importantly, buyers need to understand that the model will continue to learn through their curation, use and periodic ingestion of new data -- hence the machine learning aspect -- to ensure relevancy, accuracy and freshness over time. Buyers should evaluate a vendor's ongoing support capabilities for that effort.
Vendors love to boast about the huge number of records their engine has ingested, records gleaned from many sources and of varying types. This is fodder for the engine, the substance from which it learns and from which a workable model is created. The real value of all this is in the relevance of the output, be it recommended candidates, suggested coursework or career paths.
In some cases, though, vendors can deliver pools of talent to the buyer. This is a different matter. The number referred to previously relates to the volume of data that the engine ingested to build a reliable model for the task at hand. The second is basically a virtual data lake of potential candidates available to the buyer, filtered by the trained AI engine, which avoids the Day One problem.
The continual ingestion of new records requires that the vendor assist with ongoing data curation and algorithm checks to guard against drifts into irrelevancy or inaccuracy.
But will it integrate?
Challenges in integrating diverse products always haunt buyers. Perhaps the closest thing to good news on this front is that the code for AI engines, while not standardized, is generally very similar from engine to engine. The products included here all claim to integrate with ATSes, and many offer bidirectional integration (Eightfold AI, for one). Some companies rely on partners to augment their systems. SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting integrates with Eightfold AI, Paradox's Olivia, Skillate and JobHopin, for example. These products add AI support to the core recruiting system for areas such as intelligent matching and shortlisting, salary information, chatbots and candidate ranking.
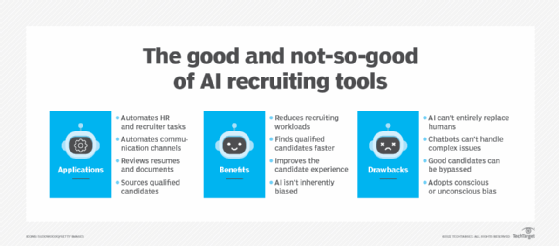
Introduction to AI recruiting tools
There are many ways to evaluate products and vendors: breadth or depth of functionality provided, technology used, price, global availability, the software's sophistication, the degrees of support and training provided, the vendor's reputation for integrity or eco-consciousness and no doubt others. Here, products that rose to the top are considered; some are total ATSes and some are talent augmenting systems.
The products reviewed in this section tend to address the needs of at least three distinct user groups: candidates, recruiters and hiring managers, and often already-hired employees. The ATSes in general all support sourcing, job posting, data parsing, candidate shortlisting or ranking, multichannel communications, career site and mobile device chatbots, and intuitive UIs geared to the needs of the candidate, hiring manager and recruiter. All deliver analytics relevant to their product scope. They also provide bot-supported scheduling of interviews and follow-up conversations, a great boon to both candidates and recruiters. Several have extended their capabilities to current employees to meet the growing demand for career growth and mobility.
Serious buyers of new AI-powered recruiting software should not neglect products from longstanding vendors such as Oracle, ICIMS and Workday. These companies are deeply vested in recruiting and talent management expertise and have the support teams, cloud infrastructure, secure platforms and deep pockets startups generally lack. While startups are still in the early stages of their product releases, these older companies have developed and refined their AI software and support for customer initiatives. They also offer more complete products, reflecting their time in the market. Many of the products reviewed here, in fact, augment rather than replace products from these established firms. A further consideration when buying AI-powered recruiting tools is vendor longevity: Will your chosen vendor be acquired by another right in the middle of your implementation?
The goal here is not to cover every feature or function; the vendors' websites have product briefs with that information. Again, because the requirements of the recruitment process are clearly defined, the products are more similar than different. Therefore, points of uniqueness or specific strengths form the basis of differentiating the vendors here, in alphabetical order, not ranked.
Arya by Leoforce
The vendor claims "Arya goes beyond conventional AI with artificial intuition, a deeper, multidimensional understanding of people, jobs and what makes them compatible," but doesn't say how the product does this. (Perhaps a clue is in the name: "Arya" means illustrious or spiritual in Sanskrit.)
Arya uses AI to source from internal databases, job boards and social networks, and provides one-click job ad placement, as do most similar products. Recruiters can engage with potential applicants via phone, text, email and bots from one integrated candidate communication dashboard. This desirable feature supports automation of personalized messages and streamlines communication throughout the entire process to facilitate contact with candidates. ATS integration is supported.
New in 2023 is a score details feature that delivers an explanation and analysis of a candidate's resume along with the overall score the system used for ranking suitability for a particular position, and Scouting Agent, an AI-driven search tool that can update candidate profiles every 24 hours. This followed the release of Candidate 360, a feature for recruiters that purports to provide a 360-degree view of a candidate's professional journey.
Arya includes candidate relationship marketing in its support for drip campaigns, a series of automated emails sent to candidates who take certain actions on a website. It can track the number of emails sent, opened, unopened and clicked, and supports one-to-one or one-to-many communication via email, text and direct dial -- features some ATSes don't have.
There are four versions. With Arya Quantum, Leoforce notably adds neurodiversity to its bias mitigation list. This should be a call-out capability in all talent acquisition products.
The Arya Pulse service provides agency-quality candidates without high staffing agency fees or long-term contracts. The cost can be as low as $599 per job to get a list of interview-ready candidates.
Another service, which signals that Leoforce is more than a software vendor, is Arya Concierge, in which the customer works with one dedicated recruiter expertly trained in using Arya to find highly compatible job candidates. Leoforce then engages with and qualifies the most compatible candidates, adding more of a traditional headhunter service to the offerings. The customer also receives all the qualified profiles Arya sourced, for future recruiting.
ICIMS Talent Cloud
ICIMS Talent Cloud deploys its AI engine to search for, opportunity match and recommend potential job candidates. Its conversational AI bot enables candidates to receive answers to FAQs, learn from employee-generated videos and schedule interviews in over 20 languages. In an attempt to make recruiter-relevant use of what may be sparse data, the digital assistant can parse an applicant's resume, creating a dynamic talent profile augmented with publicly available third-party information from external systems such as LinkedIn, if the customer has a partnership with the source, or from core HR systems. It then infers related adjacent skills the applicant may not have noted explicitly. The digital assistant integrates with communication platforms such as SMS text messaging, web chat, WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger and Microsoft Teams.
The product's intelligent search for career sites can deliver positions for applicants to consider that otherwise might not appear due to inconsistencies in spelling, acronyms or job titles. When applicants upload their resumes, Talent Cloud's AI recommends roles that align with their skills and experience.
ICIMS Talent Cloud offers the full set of recruiting and hiring analytics in an intuitive dashboard, updated regularly. Research by Apps Run the World in 2022 reported ICIMS as having the largest market share of any single ATS vendor. Oracle was second and Workday third.
Oracle Recruiting
For organizations using Oracle Cloud HCM for core HR, this closely integrated recruiting product makes sense. Thanks to its long time in the market and experience in hiring-management applications, Oracle provides sophisticated breadth and depth to address candidate relationship management and hiring management. It also applies a wealth of experience in UI creation, outshining some newer market entrants. Both traditional and generative AI span the Oracle human capital management (HCM) products, with examples as follows:
Recruiting
- Job postings. Generative AI helps create engaging job descriptions that convey a position's requirements and success criteria.
- Candidate recommendations. AI intelligent matching helps identify and recommend the best applicants for open positions, rank applicants and find similar candidates.
- Time-to-hire prediction. AI-based predictive modeling benchmarks and predicts how long it will take to fill a job based on past hires.
- Candidate summaries. Generative AI helps produce a concise summary that describes a candidate's best-fit capabilities and attributes for a position.
Skills growth and career development
- Employee profile. Generative AI helps employees develop a summary of their role and work experience for their public profile.
- Skills management. AI can keep an organization's skills inventory current, identify gaps and support talent planning decisions.
- Skills recommendations. AI offers new skill recommendations to help employees grow and develop their careers, identifies skills to advertise on job requisitions and helps candidates uncover implicit skills so they submit their best, most relevant skills on job applications.
- Career paths. AI helps employees understand their career-growth possibilities by making it easy for them to discover different career options and roles.
Performance management
- Goal setting. Each employee has a generative AI assistant that suggests goal descriptions and metrics for success.
- Performance summary. Summarizes performance reviews by analyzing multiple data sources to support performance conversations.
- Peer recognition. Generative AI drafts comments that acknowledge an employee's success in a style that aligns with the corporate culture.
HR service delivery
- Employee surveys. AI-suggested survey questions help drive higher response rates and give managers a better understanding of employee needs and sentiment.
- Support. Employees get answers and complete workflows by conversing with an AI-powered digital assistant.
- Intuitive knowledge base. Workers access a knowledge base with AI-powered search to help resolve routine inquiries.
- Knowledge management. Generative AI creates knowledgebase articles to answer frequently asked questions.
Across all its AI-enhanced products, Oracle ensures that no personally identifiable information is ingested or displayed, the platform never publishes data out of the customer's HR system and all sensitive and proprietary information is protected.
Phenom Intelligent Talent Experience
Phenom goes beyond recruiting to follow-on talent management that includes employee career pathing and support for internal mobility. The company uses "job zones" as defined by the Occupational Information Network to group jobs based on the level of preparation required, such as education, training and experience, on a scale of 1 to 5.
- Zones 1 and 2 include jobs like cashiers and drivers. The focus is on automation, giving organizations the ability to dictate where in the hiring process tasks should be automated to allow the recruiter and manager to focus on more value-adding activities. A high-volume hiring feature allows companies to engage candidates via chatbot, letting them search for jobs, apply, complete an assessment, submit a video and schedule an interview without interacting with recruiters. The assessment feature is a newer addition built by Phenom's industrial-organizational psychologists to succinctly capture the qualifications needed for frontline jobs in several industries.
- Zone 3 roles require medium preparedness, with some education and certifications such as for electricians and medical assistants.
- For zones 4 and 5, candidates need more engagement during their job search, while recruiters and managers require more AI-driven analysis during the interview process.
To improve the candidate experience, Phenom Talent Companion employs an AI chatbot that creates a streamlined but highly personalized engagement with knowledge worker candidates to find relevant jobs and get them through the application process faster.
Post-application, Interview Intelligence provides a centralized location for the hiring team to evaluate potential hires. Interviewers are provided with an AI summary of the interview, highlighting areas of interest based on the job requirements, as well as potential biases of the interviewer.
The AI assistant, Phenom X+, helps generate interview guides for keeping interviewers on track and avoiding bias or potentially illegal questions. X+ also enables recruiting teams to improve efficiency by automating repetitive tasks like scheduling interviews, adding notes to candidate profiles, drafting individual emails and generating job descriptions.
Phenom also provides customers with the tools they need to grow and retain hires. Skills are central to the technology that drives the entire platform, and they are especially relevant to Phenom's workforce intelligence system. This holistic suite of products is meant to engage employees and managers in talent management to facilitate personalized talent development, mentorships and internal mobility. With a skills ontology almost 15 years in the making, workforce intelligence makes it easy for HR to identify and fill skills gaps, managers to designate successors and promote career progression, and employees to gain visibility into opportunities that might help them excel in the organization.
All of this ties back to talent acquisition activities as well, letting recruiters employ skills technology to quickly find the best fit for an open role, whether inside or outside the organization. The AI does the heavy lifting but keeps the human in the loop by letting recruiters and managers incorporate their needs when a role opens.
Skillate
Skillate is now part of Sense, which makes AI talent engagement software for recruiting that targets the staffing industry. Skillate provides an AI-powered matching engine, chatbot screening, resume parsing and automatic interview scheduling.
Skillate starts with writing the job description itself, offering assistance by suggesting better keywords and skills. It provides the resume-to-req matching and resume parsing that are the basis of all the products reviewed here. The product collects resumes from potential sources -- such as its internal database, third-party ATSes, Google Drive, mailboxes, referrals, external agencies and career pages -- and runs incoming resumes against its machine learning model, ranking and scoring them for their fit with the job at hand. Skillate reports its AI algorithms have been trained with a data set of 120 million profiles.
First-round screening is AI-enabled here: The chatbot automatically screens the candidates for information beyond resumes, such as notice periods, intent to relocate and salary expectations.
Skillate integrates with SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting, Workday, SmartRecruiters, and Oracle Taleo.
TurboHire
TurboHire bills itself as a recruitment automation platform, adding AI to the tasks all recruiters face: job marketing and screening, interview scheduling, feedback collection, and candidate engagement and inquiry. It accommodates global and high-volume hiring through bulk email campaigns and WhatsApp and text integration. Like in other products reviewed here, customizing is possible without touching code, so recruiters can adapt it for their preferred practices. The software has an integrated agency-management portal that enables partners to contribute candidates, track their status and manage compliance, which is key to recruiting in much of Asia.
TurboHire has AI-enabled many of the standard workflows of recruiting and hiring, delivered in a series of modules. Like most such products, the focus is on productivity and efficiency. The company claims to have automated 85% of manual recruiting activities. Its platform integrates with solutions from companies such as Oracle and SAP SuccessFactors. Single sign-on is accommodated with Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workspace.
AI in talent sourcing
Locating potential employees, especially passive candidates, is its own challenge. Products that use AI in sourcing have the advantage of searching huge and widespread sources of talent almost instantly. While this kind of AI is part of most ATSes, some products that augment ATSes are worth calling out. As the first product offerings from their respective vendors, these may grow into full-fledged ATSes over time, be acquired and added to an ATS player's product, or remain as a separate tool for at least the short term.
Fetcher
If there were a reward for clever product names, Fetcher might win because it does just that: fetches potential applicants. Fetcher is a candidate sourcing and scheduling tool with the recruiting analytics buyers expect. Used by small businesses with English-only needs, it identifies candidates based on AI-powered keyword matches. Over time, it learns a company's candidate preferences and then identifies potential talent accordingly.
The platform automates the standard requirements for email outreach campaigns, provides a duplication option to reuse previous search criteria and has a notes feature for recruiter feedback. The information provided is piped directly to the vendor's internal teams, to further tailor the search, enhance the algorithms and help Fetcher find and deliver the candidates sought. The scheduling plugin allows for rapid company-branded scheduling of telephone screens and interviews.
While the sourcing functions of this product are not unique, it is nonetheless an intuitive tool for recruiters in small businesses. It integrates out of the box with Ashby, Fountain, Greenhouse, Lever, JazzHR, Oracle Taleo, Recruitee, SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting, SmartRecruiters and Teamtailor.
SeekOut
SeekOut provides an AI-powered talent search engine to help recruiters quickly find and hire the most qualified passive candidates. It appears to be Boolean-based, a potentially limiting approach that can be hard to use. The company says it provides access to hundreds of millions of candidates from potentially untapped talent pools, including public profiles, GitHub, the papers and patents of experts, employee referrals, company alumni and candidates already in the organization's ATS. There are more than 100 searchable fields that include skill sets, background, experience, education and diversity, as well as fields such as security clearance, which is useful for U.S. federal government positions. A healthcare talent pool, for example, includes 5.5 million healthcare professionals. In all, the company claims to have over 800 million public profiles, 330 million of which are underrepresented candidates.
SeekOut supports the concept of a total talent pool as well as individuals. Recruiters can see total amalgamated talent by location and specific people with that talent in that location. This is a potentially valuable feature many other platforms lack.
SeekOut's ability to locate and screen tech talent should be a draw for organizations that need technologists. From GitHub, the app can provide and review actual code to better evaluate a potential applicant's technical prowess. It appears to be easy and intuitive to use, albeit with a slightly underwhelming UI for people accustomed to today's glitzier applications, and is definitely worth considering.
XOR AI Recruiter
Much of the recruiting industry focuses on white-collar and professional hiring and only adds large-volume hiring as an afterthought, often glossing over this important employee segment. Addressing this, XOR says it provides a digital recruiting assistant that enables its platform to deliver blue-collar workers for only $500 a hire in less than five days.
XOR AI Recruiter employs the natural language processing (NLP) capabilities of ChatGPT to provide a conversational recruiter chatbot and consolidated communication platform with tools for text messaging, WhatsApp, live chat, phone calls and video to drive engagement. It uses the AI chatbots to automate repetitive tasks such as screening, scheduling, reengagement, onboarding and rehiring. Availability in more than 100 languages enhances its use for multinational corporations -- for example, Ikea is a customer.
It offers bidirectional integration with several prominent ATS systems. XOR sources candidates from job boards, text conversations, career sites, the ATS itself and, with added extensions, other websites.
XOR AI Recruiter is more of an automated service than a purchasable product. In addition to targeted digital marketing for advertising campaigns and virtual career fairs, the vendor uses nonconventional sourcing channels, such as multilevel referral programs, and relies on influencers in local communities to spread the word about hot job openings and motivate candidates to apply. The XOR system then connects and interacts with the candidate directly rather than through job boards.
Similar to the functionality of other products discussed here, once recruiters select the essential requirements for candidates, XOR AI Recruiter will screen them, assign scores and automatically schedule and remind them about their upcoming interview.
Skills-based talent decisions for today and tomorrow
Few areas are getting more attention from business executives than skills. It's the ground zero of talent management, and fears about the skills gap are deep-seated. The pandemic didn't help, as many companies failed to use the time to upskill employees. The supposed Great Resignation (the baby-boom generation retiring), the perception that high school and college graduates lack necessary skills, and the advent of new technologies that require new, different and often sophisticated skills have all contributed to a skill malaise. Reskilling has been a hot topic, but little evidence of widespread results has been forthcoming.
The issue is longstanding. Traditional HR systems of record have disparate data about each candidate and employee that is often fragmented across systems and self-reported based on each person's recollection of what they accomplished. It never encapsulates the depth and breadth of what they have done -- and most certainly does not yield insight into their potential. Businesses know frightfully little about the skills their employees really have, and often even the exact skills the business needs.
Here are two noteworthy products, among many in the market, that use AI in ascertaining and improving skills.
Eightfold AI Talent Intelligence suite
Eightfold calls its product a talent intelligence platform that enables "holistic" talent strategies, and it could be among the first of an emerging product category. Eightfold has a proprietary global data set of more than 1.5 billion talent profiles from which its AI generates recommendations to help employers decide how and when to build, buy or borrow talent. It employs a skills-based framework that matches people to opportunities, including full-time, part-time, project and gig work. Eightfold uses that data to understand the availability, maturity, relevance, learnability and evolution of skills in specific organizations and throughout the global market.
Eightfold's Job Intelligence Engine powers skills-based talent decisions about the job requirements needed for every role in an organization. This skills-based approach drives decision-making around upskilling, reskilling, hiring, staffing of contractors and attaining diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) goals. Additionally, the job intelligence engine examines skill adjacency and context to determine future capabilities and needs as organizations grow. The platform also enables self-learning, data-driven updates that help to ensure consistent, unbiased evaluations of individual capabilities and ability to learn against globally standardized job descriptions and requirements.
One of the products in the Eightfold platform, Eightfold Talent Management, is available in more than 24 languages. Employees can use it to find reskilling and upskilling opportunities across courses, mentors and projects based on current skills and career aspirations. The goal of people developing their own skills and assuming responsibility for their career growth is addressed through curated opportunities for continuous learning. By using Eightfold, organizations can better understand the potential of their workforce on a global scale and guide individual employees to further learning, skill development and career opportunities.
Eightfold integrates with Workday, SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting, Oracle Taleo, Oracle Recruiting Cloud, Greenhouse and others.
Fuel50
Most of the products that play a part in recruiting begin with the job or role. Fuel50 turns that premise on its head, looking first at the skills across the organization and how to better position them. This requires reviewing every job description and updating it with the talents and skills needed for each role, rather than the degrees, years of experience and certifications required. Fuel50 helps people identify their talents and skills and supports their growth with career development actions, feedback and learning. The result is not just internal talent mobility but also workforce agility.
A woman-owned company founded by Anne Fulton, Fuel50 provides an AI-driven talent marketplace that also fuels engagement and employee retention with global coverage. Its tool helps organizations understand their bench strength, build talent pipelines, predict skills shortages and conduct workforce mapping.
Fuel50's AI architecture uses validated career frameworks to fast-track the rebuilding of an organization's career framework to eliminate the manual process of creating and maintaining job profiles, which change often in growing companies.
Other notables
Dozens and dozens of stellar AI products for talent acquisition and longer-term talent management are not complete ATSes yet definitely merit consideration. Here's a sample of those that have risen to the top.
HireVue
HireVue calls its product a "talent experience platform" designed to automate workflows and scale hiring. Long noted for its video interview capabilities, HireVue has made them less bias-prone by using natural language translation to provide a transcript for hiring managers and recruiters. The process creates a blind interview and eliminates potential discrimination by race, gender, color, appearance, dialect, name, age, etc.
HireVue's AI recruiting assistant bot is text-only and provides chat-based job matching. It supports mobile devices and smartwatches via text messaging and WhatsApp.
However, what merits attention here is the vendor's documentation, which is prominently placed on its website. HireVue has done something I have nagged vendors about for half a decade: explain how its AI engine works to mitigate adverse impact on protected groups. It has articulated a very clear, detailed and understandable "Explainability Statement" providing the transparency that is essential when using AI-based products for hiring and assessment. In addition, a second statement, "Bias, AI ethics and the HireVue approach," documents HireVue's approach to ethical AI in online hiring.
Every purveyor of AI in talent acquisition should make sure buyers have such an understanding.
Paradox
My favorite part of Paradox, I confess, is Olivia, a multilingual recruiting assistant chatbot named after the founder's spouse. I am putting Olivia in the best bot category. According to the company, Olivia can answer tens of thousands of candidate or employee questions accurately, consistently and at any time of the day. As with all the talent acquisition bots included here, Olivia was developed as an assistant to offload repetitive chores and question answering from busy recruiters. This she does, but Olivia also solves the logistical challenge of interview scheduling and can review hundreds of hiring managers' calendars to schedule interviews in seconds. The bot's automated text reminders help to reduce interview cancellations and no-shows, potentially saving time for recruiters. Olivia can also schedule large events, onboarding sessions, seasonal hiring and orientation, and manage registration and reminders.
While Olivia offloads work for recruiters, the Experience Assistant focuses on the potential applicant. Apparently now part of a bot team with Experience Assistant, Olivia becomes a dynamic content-discovery engine that makes any career site experience feel like it was built specifically for that candidate, allowing personalized interaction on mobile and desktop devices. When people start a conversation with Olivia, the chatbot uses candidate responses, geolocation, resume data and more to create an immersive, hyper-personalized experience that serves only the most relevant jobs and content to each person. The experience works with any career site provider and provides the UI that candidates have come to expect on consumer apps like Instagram and Snapchat.
In a slightly different vein, after acquiring Traitify, a personality data company that was building the personality data genome for the employment marketplace, Paradox debuted Animated Assessment. Starring a character named Ash, the two-minute mobile phone app measures a person's openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness and neuroticism through "me" and "not me" responses. Recruiters can then use the results in ascertaining the fit with their current openings.
An AI caveat for buyers
If you are in the market for a new talent acquisition system or are augmenting an existing system, you will very likely be looking at a product that has AI. AI capabilities can greatly assist recruiters and hiring managers because of the speed and accuracy with which open reqs can be addressed. But as mentioned, buying a product with the machine learning you need means it is not necessarily plug-and-play. Most buyers need training and assistance with the ongoing learning that the AI will have to do to ensure that the requirements of the specific organization are addressed, DEI goals are met and the system doesn't go rogue or lose relevancy over time.
This means carefully evaluating the vendor in addition to the product by asking the following questions:
- How large is the support team that works with each customer on their organizationally specific machine learning?
- How often is the system refreshed with new learning?
- What is the AI development team's roadmap for the year ahead?
- Will AI-savvy support teams be spread too thin to accommodate a growing customer base?
- What customer education is provided about how the system works?
- How does the vendor support the AI transparency essential to explainability?
- What is the model for anomaly detection?
- How often do the vendor's data scientists monitor the system for signs it has drifted away from intended outcomes?
There is yet another point vital to technology considerations. A study by Madeline Laurano, founder of Aptitude Research, found that one in two recruiters would join another organization if it had better technology. (The study also reported that one in three recruiters were looking for new jobs.) Dated talent acquisition software can well lead to attrition in an organization's recruiting professionals.
An AI caveat for recruiters
Recruiters obviously aren't the only ones with access to AI. Applicants also have easy, cost-free access and can use generative AI and other tools to their benefit -- and in some cases, to the detriment of recruiters. Resumes can be more easily tailored to the job at hand (which can be good) but an applicant can also figure out how to apply for hundreds, even thousands, of jobs at once, which makes gauging actual interest difficult.
Conclusion
The quest for superior talent is never-ending. Through smart technology choices that include AI, machine learning and NLP, recruiters will be able to accomplish this faster and more easily. As important, through wise purchasing decisions, they can also ensure their ability to ethically hire a diverse employee base.
Today's tools cover every aspect of talent acquisition, from recruitment marketing to sourcing, job description management, candidate assessment and pre-screening; recommending other positions in an organization to qualified applicants; offer and rejection management; skill assessment; and career and learning assistance and direction -- all with far more sophisticated analytics than were available in the past.
AI in talent acquisition can provide a hands-free approach to time-intensive tasks such as interview scheduling and initial qualification screening, much like robots in factory-floor automation. Currently, however, the technology is applied more as helping hands, adding speed and efficiency to the same work recruiters have always done. While this may help organizations get by with fewer recruiters, it also can support scenarios where ...
Comments
Post a Comment